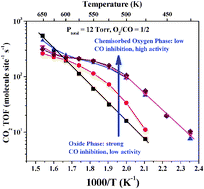
CO oxidation was carried out over Ru(0001) and RuO2(110) thin film grown on Ru(0001) at various O2/CO ratios near atmospheric pressures. Reaction kinetics, coupled with in situ polarization modulation infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy (PM-IRAS) and post-reaction Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) measurements, were used to identify the catalytically relevant phases under different reaction conditions. Under stoichiometric and reducing conditions at all reaction temperatures, as well as net-oxidizing reaction conditions below ∼475 K, a reduced metallic phase with chemisorbed oxygen is the thermodynamically stable and catalytically active phase. On this surface CO oxidation occurs at surface defect sites, for example step edges. Only under net-oxidizing reaction conditions and above ∼475 K is the RuO2 thin film grown on metallic Ru stable and active. However, RuO2 is not active itself without the existence of the metal substrate, suggesting the importance of a strong metal–substrate interaction (SMSI).