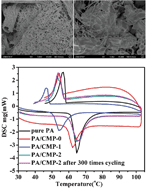
Conjugated microporous polymers (CMPs) with large BET surface areas were used as porous supporting materials to prepare form-stable phase change material (PCM) composites. Due to the unique superoleophilicity of CMPs, PCMs could be absorbed spontaneously into CMPs and can stay stable in the CMP samples without leakage even over their melting points. Results obtained from X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) show that the incorporation of CMPs decreases the crystal size of PCMs in the composites. The latent heat of CMP/PCM composites was measured ranging from 103.3 kJ kg−1 to 171.0 kJ kg−1. The resulting PCM composites show excellent recyclability and thermal stability after 300 melting and freezing cycles, and have great potential for renewable energy saving applications.