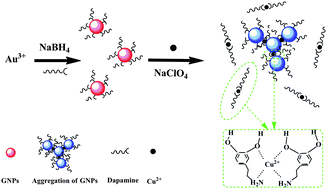
A facile, economic and eco-friendly colorimetric detection method for dopamine has been well-established in this paper. It is based on the interaction between Cu2+ ions with amino group and hydroxyl groups of the dopamine adsorbed on the surface of gold nanoparticles (GNPs). Cu2+ ions serve as the selective “discriminator and linker” for dopamine detection. At high ionic strength, introduction of Cu2+ ions to GNPs solution including dopamine arouses the aggregation of GNPs, the color of the solution changes from wine red to blue, and the red shift of ultraviolet absorption peaks. The concentration of dopamine can be determined by monitoring with the naked eye or a UV-vis spectrometer. The calibration curve showed that the absorption ratio value at 650 and 525 nm (A650/A525) increased linearly over the dopamine concentration range of 5 × 10−7 M to 1 × 10−5 M with a limit of detection of 2 × 10−7 M (3σ). This method exhibits excellent selectivity for dopamine over other α-amino acids, glutathione, glucose, uric acid and ascorbic acid, and the process of the experiment, including the preparation of GNPs, detection of dopamine, pretreatment of sample, is finished within 30 min at room temperature. On the other hand, this probe was successfully applied to detect dopamine in human serum with high sensitivity, and this strategy may provide a selective sensing approach for measuring dopamine under physiological conditions.