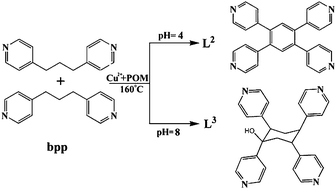
Two novel metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based on different tetradentate in situ ligands, CuI3(L1)2(L2)[PMoVI8VV4O40(VIVO)2]·2H2O (1) and [CuI2Cl2(L3)] (2) (L1 = 1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene, L2 = 1,2,4,5-tetra(4-pyridyl)-benzene L3 = a-1-hydroxy-e,e,e,e-1,2,4,5-tetra(4-pyridyl)cyclohexane) have been rationally hydrothermally synthesized and characterized by elemental analyses, IR spectroscopy, TG analyses, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction, respectively. Here, compound 1 represents the first example that dehydrogenative coupling has been employed to yield a novel tetradentate coplanar dye molecule in POM-based MOFs. It also exhibits unique 3D MOFs with two topologies (4284)(4283101)(86)2 and (4383)(4284)(446289)(4106183) due to different definitions of nodes. Compound 2 shows a two-fold diagonal/diagonal inclined interpenetration based on CuI ions and in situ synthesized ligands L3. Interestingly, reaction conditions play important roles in the domination of in situ ligands (L2 and L3) from the same precursor bpp (bpp = 1,3-bis(4-pyridyl)propane). Additionally, electrochemical and photocatalysis properties of compound 1 have also been minutely investigated.