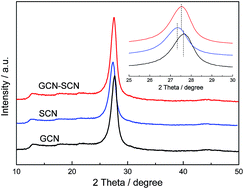
In heterojunction catalysts, the potential difference is the main driving force for efficient charge separation and transfer. The slight difference in the electronic band structure of the isotype heterojunction catalysts causes a poor driving force, leading to a dissatisfactory charge separation efficiency. In this work, g-C3N4/S-g-C3N4 metal-free isotype heterojunction catalysts (GCN–SCN) with an enhanced charge driving force were prepared by a two step calcination method. Anoxic photocatalytic degradation of RhB under visible light was used to evaluate the performance of the as-prepared g-C3N4 catalysts. The results indicate that this two step calcination method can markedly improve the charge driving force of the as-prepared isotype heterojunctions, leading to a more efficient charge-carrier migration. GCN–SCN displays the highest reaction rate constant of 0.0228 min−1, which is 3.5 and 2.9 times higher than that of GCN/SCN(1) and GCN/SCN(2) prepared by a one step calcination method. A linear relationship is observed between the VB driving force and RhB degradation rate. This paper provides a new perspective to prepare isotype heterojunctions with an improved charge driving force and photocatalytic performance.