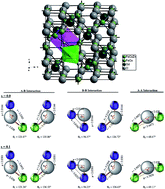
Rare earth (RE) ions are known to improve the magnetic interactions in spinel ferrites if they are accommodated in the lattice, whereas the formation of a secondary phase leads to the degradation of the magnetic properties of materials. Therefore, it is necessary to solubilize the RE ions in a spinel lattice to get the most benefit. In this context, this work describes the synthesis of Co–Zn ferrite nanoparticles and the Gd3+ doping effect on the tuning of their magnetic properties. The modified sol–gel synthesis approach offered a facile way to synthesize ferrite nanoparticles using water as the solvent. X-ray diffraction with Rietveld refinement confirmed that both pure Co–Zn ferrite and Gd3+ substituted Co–Zn ferrite maintained single-phase cubic spinel structures. Energy dispersive spectroscopy was used to determine the elemental compositions of the nanoparticles. Field and temperature dependent magnetic characteristics were measured by employing a vibration sample magnetometer in field cooled (FC)/zero field cooled (ZFC) modes. Magnetic interactions were also determined by Mössbauer spectroscopy. The saturation magnetization and coercivity of Co–Zn ferrite were improved with the Gd3+ substitution due to the Gd3+ (4f7)–Fe3+ (3d5) interactions. The increase in magnetization and coercivity makes these Gd3+ substituted materials applicable for use in magnetic recording media and permanent magnets.