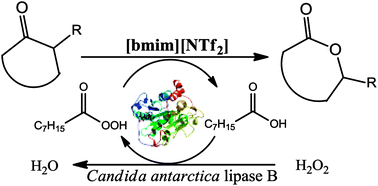
A new method for the chemo-enzymatic Baeyer–Villiger oxidation of cyclic ketones to lactones has been developed. The influence of reaction parameters and the structure of various ionic liquids were studied. Free Candida antarctica lipase B or Novozyme-435 suspended in an ionic liquid was used as the catalytic phase. The reaction was carried out under mild conditions at room temperature using 30% aq. H2O2 as the oxidation agent. 1-Butyl-3-methyl bistriflimide was the most effective ionic liquid and increased the reaction rate compared to toluene. Lipase exhibited good stability, and the ionic liquid could be easily reused. Therefore, a general chemo-enzymatic method for the oxidation of cyclohexanones and cyclobutanones to obtain adequate lactones in high yields (79–95%) has been proposed.