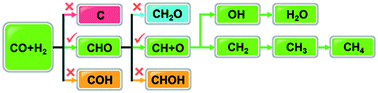
CO methanation is an industrially important reaction for the removal of trace amounts of CO from the hydrogen feed for ammonia production and in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Although the H-assisted CO dissociation mechanism has been extensively elucidated, discrepancies exist in determining through which C1-oxygenate intermediates the C–O bonds are broken. Using density functional theory calculations and microkinetic studies, we show that theoretical studies can reach agreement in C–O bond scission via the CHO intermediate on Co(0001) at a low coverage regime, and this mainly controls the CO methanation rate. This mechanism is independent of the functionals considered and the presence of graphitic carbon, and likely also pertains to other Co surface structures, including some open facets and step sites. The work provides fundamental insights into the mechanistic discrepancies relating to CO activation and methanation on hexagonal close-packed Co catalysts, which can potentially be used to design improved CO hydrogenation catalysts.