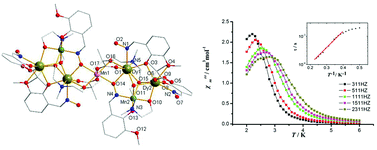
Using 3-methyloxysalicylaldoxime (mosaoH2) and N-methyl diethanolamine (N-mdeaH2) as coligands, a family of heptanuclear Mn/Ln heterometallic compounds [MnIIMnIII2LnIII4(mosao)2(mosaoH)4(piv)4(N-mdea)4]·xMeCN [Ln = Dy(1), Tb(2) and Y(3), pivH = pivalic acid] have been prepared. The crystal structures of 1–3 were obtained, and their core consists of two MnIIILn2(μ3-OR)2 (RO2− = N-mdea2−) triangles linked to a central MnII atom. A dc magnetic susceptibility study reveals that single-ion effects of the Ln ions are dominant in compounds 1 and 2. As for compound 3, which contains diamagnetic Y ions, the magnetic interactions between Mn ions via oximate NO bridges are revealed to be ferromagnetic. Fitting of the χmT vs. T data gives g = 1.96 and J = 1.12 cm−1, affording a S = 13/2 ground state. All of the three compounds exhibit frequency-dependent out-of-phase ac susceptibility signals indicative of slow magnetization relaxation and potential SMM behavior. Among them, 1 and 3 display the out-of-phase χ′′m peak maximum above 2.0 K. Fitting of the ac susceptibility data to the Arrhenius law gives an energy barrier Ueff = 9.27/13.83 K for 1 and 3, respectively.