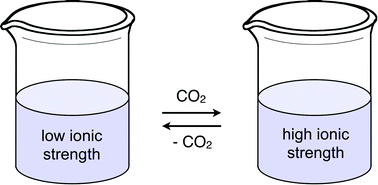
The practice of adding salt to water to induce salting out of contaminants or to break emulsions and suspensions is generally avoided industrially because of the expense of the necessary treatment of the salty water afterwards. However, the use of switchable water, an aqueous solvent with switchable ionic strength, allows for reversible generation and elimination of salts in aqueous solution, through the introduction and removal of CO2. In the effort to improve the efficiency of these switchable salts, a physical study modeling their reactivity and solution behaviour has been performed, resulting in a set of design principles for future switchable water additives. The resulting polyamines synthesized using this template show the highest efficiency recorded for a switchable water additive.