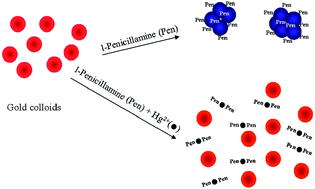
This study proposes a dynamic anti-aggregation sensing method for detecting mercury(II) ions in aqueous solutions. The proposed method is based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in the presence of an aggregation agent inhibited by Hg2+ because of high affinities between the mercury(II) ions and the aggregation agents. The aggregation agents tend to coordinate with Hg2+ rather than be absorbed onto the AuNP surfaces, causing the size and axial ratio of the retained gold nanocolloids to be mostly unaffected. Because the extinction maxima are affected by the size, axial ratio, and morphologies of gold nanoaggregates, mercury(II) ions can be detected by comparing the extinction spectra of gold nanocolloids in both the presence and absence of mercury(II) ions. The proposed sensing method demonstrates the advantage of requiring no surface modification of AuNPs, and enables rapid detection with acceptable sensitivity and selectivity. Under optimized conditions, the detection limit toward Hg2+ is ca. 25 nM.