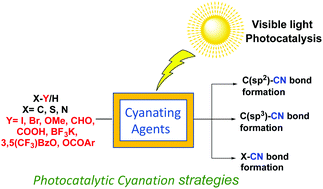
Photoredox chemistry has emerged as an efficient tool in catalyzing organic reactions as it utilizes light as an energy source without any external initiator or reagent. The cyanide group is one of the most crucial organic scaffolds as it is present in various bioactive and pharmaceutical drugs and has the ability to be converted to other multiple functional groups. In the last few years, a great advancement has been achieved in photocatalytic cyanation strategies in terms of homogeneous and heterogeneous photocatalysis. This review summarizes various photochemical strategies in C–CN, X–CN (X = N, S), and non-cyanide R–CN bond formation.