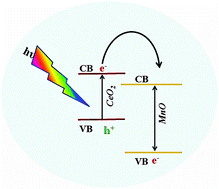
CeO2–MnO composite thin films have been deposited on glass substrates, which were coated with fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO), by aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition (AACVD) using a 1 : 1 mixture of the cerium complex [Ce(OCOCF3)4]−[(CH3)2NHCH2CH2OH]+ (1) and acetatomanganese(II). X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy and profilometry were used to investigate the phase purity, stoichiometry and thickness of the films. EDX results confirmed that the Ce : Mn ratio was 1 : 9 in the deposited composite thin films. FEG-SEM analysis illustrated that the morphology of the fabricated films was influenced by the deposition temperature and hence the optoelectronic properties. UV-vis studies of a composite thin film fabricated from methanol solution at 475 °C demonstrate a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. From its current–voltage characteristics it is evident that a CeO2–MnO composite semiconductor electrode exhibits n-type behavior and the photocurrent was strongly dependent on the deposition temperature. A CeO2–MnO photoanode deposited at 475 °C for 45 min from a 0.023 M solution of (1) and acetatomanganese(II) in methanol gave a maximum photocurrent density of 265 μA cm−2 at 0.65 V vs. Ag/AgCl/3 M KCl using a 0.5 M NaOH electrolyte.