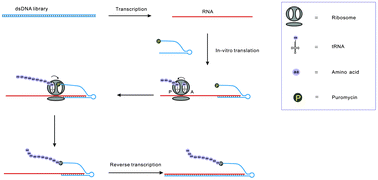
A novel DNA display strategy, based on a new puromycin modifier, has been developed. The 5′-end puromycin-tethered oligonucleotide was synthesized to hybridize with mRNA, so that it could attack the nascent polypeptides during in vitro translation. The DNA–peptide fusion molecule can tolerate more harsh and stringent selection conditions, therefore, this DNA display may become a useful tool for in vitro display technologies for the selection of peptide drug candidates.