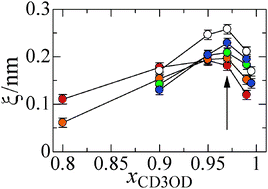
Effects of the alkyl-chain length of the imidazolium cation on the mixing state of imidazolium-based ionic liquids, 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium (Cnmim+, the alkyl-chain lengths n of 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12) bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide (TFSA−), and methanol were investigated using small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), attenuated total reflectance infrared (ATR-IR), and NMR techniques. SANS measurements revealed that Cnmim+TFSA− is heterogeneously mixed with methanol in the methanol mole fraction range of 0.8 ≤ xCD3OD ≤ 0.995. The heterogeneity of the Cnmim+TFSA−–methanol solutions, except for C4mim+TFSA−, is most enhanced at xCD3OD ≈ 0.97 over the entire mole fraction range. Thus, the mole fraction at the maximum heterogeneity of the solutions is independent of the alkyl-chain length. In contrast, the magnitude of the maximum heterogeneity of the solutions is larger in the order of the alkyl-chain length from n = 4 to 12. ATR-IR and NMR measurements showed that methanol molecules gradually form hydrogen bonds among them in the solutions with increasing xCH3OH. In particular, the hydrogen-bonds among methanol molecules are conspicuously evolved in the solutions above xCH3OH ≈ 0.8. The increase in the concentration of the hydrogen-bonded methanol with increasing xCH3OH does not significantly depend on the alkyl-chain length. According to these results, we concluded that the heterogeneity of Cnmim+TFSA−–methanol solutions arises from polar domains composed of the imidazolium rings, TFSA−, and methanol clusters and nonpolar domains formed by interaction among the alkyl chains of the imidazolium cations.