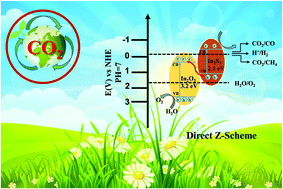
The photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide into chemical fuels has great practical significance in solving the energy crisis and issues associated with environmental pollution, but it remains a big challenge owing to its low light absorption rate, sluggish charge separation/transfer efficiency, and poor stability of existing photocatalysts. Heterogeneous composites are promising in solving the problems of sunlight absorption and carrier separation in photocatalysis. In this study, a direct Z-scheme Sn-In2O3/In2S3 heterogeneous photocatalyst was constructed by chemical vapor deposition and vapor phase sulfuration. An optimized photocatalyst with Pt as a co-catalyst shows efficient photocatalytic activity in carbon dioxide reduction. The CH4 yield rate reached 0.41 μmol cm−2 h−1, and the CO yield rate is as high as 1.03 μmol cm−2 h−1. The favorable photoelectrochemical performance was attributed to the effective light absorption of In2S3 and improved charge transfer efficiency due to the direct Z-scheme structure of the composite photocatalyst. This work provides new ideas in the preparation of highly efficient recyclable photocatalytic systems by constructing Z-scheme nanostructured heterojunctions.