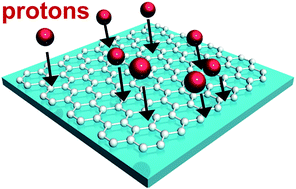
Monolayer graphenes were irradiated with 5–15 MeV high-energy protons at various doses from 1 × 1016 to 3 × 1016 cm−2, and their characteristics were systematically investigated using micro-Raman spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). As the energy and dose of the proton irradiation increased, the defects induced in the graphene layers also increased gradually. The average defect distances of 10 MeV proton-irradiated graphene decreased to 29 ± 5 nm at a dose of 3 × 1016 cm−2. The defect formation energies for various types of defects were compared by using density functional theory calculation. After proton irradiation, the results of micro-Raman scattering and XPS indicated p-doping effects due to adsorption of environmental molecules on the damaged graphene. Our results show a direct relationship between the defect formation of the graphene layers and the energy/dose of the proton irradiation.