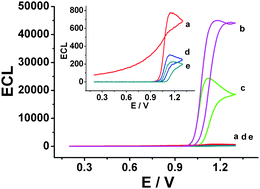
In this study, we report the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) of tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) (Ru(bpy)32+) in the presence of hydrazine and its derivatives in solution phase for the first time. Hydrazine and isoniazid were found to be able to enhance the ECL of Ru(bpy)32+, while phenylhydrazine and hydroxylamine were observed to decrease the ECL. The possible ECL mechanisms are discussed, and the method was used to detect hydrazine and isoniazid in aqueous solutions. Under the optimum experimental conditions, the dynamic ranges were 10−7–10−3 M and 10−6–10−3 M for hydrazine and isoniazid, respectively. The detection limits were 3.8 × 10−8 M for hydrazine and 4.8 × 10−7 M for isoniazid. The proposed method has been applied to detect the content of isoniazid in pharmaceutical samples with satisfactory results.