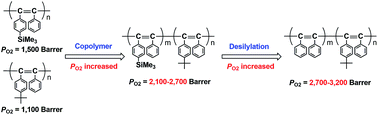
Diphenylacetylenes having various silyl groups [PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC6H4-R; R = p-SiMe3 (TMSDPA), p-SiEt3 (TESDPA), p-SiMe2-n-C8H17 (DMOSDPA), and p-SiPh3 (TPSDPA)] were copolymerized with diphenylacetylene having a tert-butyl group (PhC
CC6H4-R; R = p-SiMe3 (TMSDPA), p-SiEt3 (TESDPA), p-SiMe2-n-C8H17 (DMOSDPA), and p-SiPh3 (TPSDPA)] were copolymerized with diphenylacetylene having a tert-butyl group (PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC6H4-tertBu; TBDPA) using a TaCl5–n-Bu4Sn catalyst in various monomer feed ratios to provide high-molecular-weight copolymers in high yields. The free-standing membranes were fabricated by solution-casting, except poly(TPSDPA-co-TBDPA). Interestingly, the gas permeability of poly(TMSDPA-co-TBDPA) was higher than those of the homopolymers, poly(TMSDPA) and poly(TBDPA). The permeability of the copolymers became lower as the silyl groups became bulkier. The desilylation of membranes was carried out using a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid/hexane. When bulkier silyl groups were removed, the oxygen permeability increased to larger extents. The oxygen permeability coefficients of the copolymers and desilylated copolymers increased with increasing composition ratio of TBDPA. The gas diffusivity and gas solubility were also increased upon desilylation.
CC6H4-tertBu; TBDPA) using a TaCl5–n-Bu4Sn catalyst in various monomer feed ratios to provide high-molecular-weight copolymers in high yields. The free-standing membranes were fabricated by solution-casting, except poly(TPSDPA-co-TBDPA). Interestingly, the gas permeability of poly(TMSDPA-co-TBDPA) was higher than those of the homopolymers, poly(TMSDPA) and poly(TBDPA). The permeability of the copolymers became lower as the silyl groups became bulkier. The desilylation of membranes was carried out using a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid/hexane. When bulkier silyl groups were removed, the oxygen permeability increased to larger extents. The oxygen permeability coefficients of the copolymers and desilylated copolymers increased with increasing composition ratio of TBDPA. The gas diffusivity and gas solubility were also increased upon desilylation.