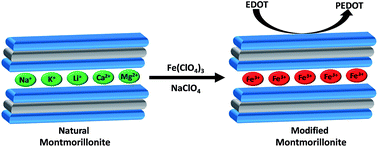
Modification of natural montmorillonite can be achieved efficiently through Fe3+ fixation using solutions of Fe(ClO4)3 in NaClO4. An analysis of the process by a pseudo-second order model allowed us to establish that Fe3+ sorption into montmorillonite is a chemical process that involves an exchange of cations from the montmorillonite interstitial space between layers. The presence of Fe3+ on the interstitial space between layers was determinated by XPS (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy). The oxidant properties of the modified montmorillonite were evaluated by the polymerisation of ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) to generate polyethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT)–clay, which is a semiconductor material.