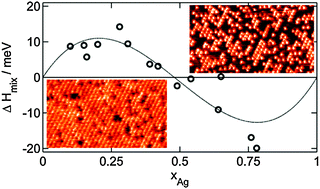
The formation and atom distribution in two-dimensional PdxAg1−x/Pd(111) monolayer surface alloys were studied by high resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) with chemical contrast. From short-range order (SRO) parameters, we calculate preferences for like or unlike nearest neighbours to elucidate the mixing behaviour of the two components for various sub monolayer Ag surface contents. In the regime of low Ag surface contents (<40% Ag), the system shows a weak tendency towards phase separation, high Ag coverages (>60% Ag) result in a disperse distribution of the atoms in the surface. Effective pair interactions (EPIs) were derived by comparing the measured distribution with distributions obtained using Monte Carlo (MC) simulations. From the EPIs, we derived a function for the mixing energy, which can describe the change from clustering to a disperse distribution. The effects of the resulting surface atom distributions and of the Ag coverage dependent surface mixing/demixing on catalytic reactions are discussed.