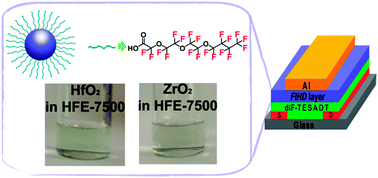
We report the synthesis and characterisation of fluorous-inorganic hybrid dielectric (FIHD) materials processable in highly fluorinated orthogonal solvents for printed electronic devices. FIHD materials were prepared successfully via ligand exchange reactions between organic ligands on the surfaces of nanomaterials and highly fluorinated carboxylic acids. When hafnium oxide (HfO2) or zirconium oxide (ZrO2) nanoparticles stabilized with trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) were treated with perfluoro-3,6,9-trioxatridecanoic acid in HFE-7500 at 130 °C, the modified surface characteristics of the nanoparticles resulted in excellent solubilities in the fluorous solvent. The dielectric constant of HfO2 and ZrO2 nanoparticles modified with fluorous acid was ca. 4.4 and 4.3 at 1 KHz, respectively, which is significantly higher than that of fluoropolymers. Top-gate organic thin film transistors (OTFTs) were fabricated using solution-processed organic semiconductors and HfO2-based FIHD materials. The hole mobilities of the OTFTs produced were as high as 0.08 cm2 V−1 s−1 (Vds = −40 V) and the on/off ratio reached 3.3 × 106 when 2,8-difluoro-5,11-bis(triethylsilylethynyl)anthradithiophene (diF-TESADT) was employed as the semiconductor layer. These device performances demonstrate that FIHD materials can be useful components for general printed electronic devices processed with soluble organic electronic materials.