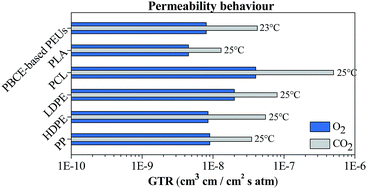
A family of poly(ester urethane)s obtained by chain extending hydroxyl-terminated polyester prepolymers has been studied. Poly(butylene cyclohexanedicarboxylate) has been coupled in different mass ratios with two poly(butylene succinate)-based random copolymers containing ether linkages. So, five high molecular weight bio-based poly(ester urethane)s have been designed. The effect of the chemical structure and of the mass ratio of the two blocks in the final polymer has been evaluated by characterizing the materials from a molecular, thermal and mechanical point of view. In addition, envisioning a food packaging application, biodegradation in compost and measurement of the gas barrier properties have been carried out and correlated to the polymer chemical structure. The activation energy of the gas permeation process has been calculated, too. The results highlight that through the adopted strategy it is possible to prepare a new class of promising materials whose properties can be easily tailored by acting on two parameters: the mass ratio between the two prepolymers in the final material and the chemical structure of each block.