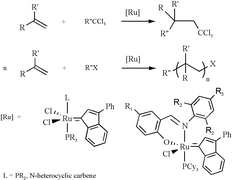
Ruthenium indenylidene complexes provide a new class of versatile catalysts for promoting the Atom Transfer Radical Addition (ATRA) of carbon tetrachloride and chloroform toward a whole array of olefins such as acrylates, methacrylates, styrene and 1-octene. The reaction was successfully extended to an Atom Transfer Radical Polymerisation (ATRP) process by changing the monomer/halide ratio. The polymerisation reaction can be accelerated by adding n-Bu2NH to the reaction mixture. However this leads to an uncontrolled polymerisation. Further improvements to the catalytic activity can be made by transforming the Ru complexes in the cationic 14-electron species or exchanging the indenylidene fragment with an ethoxycarbene. A very high activity is reached when these complexes are exposed to methyl methacrylate in aqueous media while maintaining excellent control over the formed polymers.