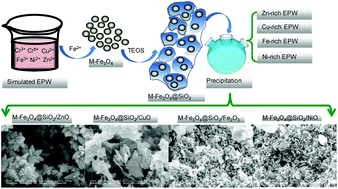
Heavy metal recovery is a promising way to reduce the pollution from electroplating wastewater (EPW), and magnetite photocatalysts of mixed-ferrite (M-Fe3O4)@SiO2/metal oxides have been prepared to reuse heavy metals from simulated-EPW (S-EPW) and real-EPW (R-EPW). In this work, four pure magnetite photocatalysts M-Fe3O4@SiO2/ZnO, M-Fe3O4@SiO2/CuO, M-Fe3O4@SiO2/Fe2O3, and M-Fe3O4@SiO2/NiO were synthesized via a simple precipitation reaction, where the M-Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles served as the magnetic cores and supports for the metal oxides. The structures, morphologies, and magnetic properties of these magnetite photocatalysts were characterized, and then the photocatalytic performances of the pure and complex magnetite photocatalysts (M-Fe3O4@SiO2 supported single and mixed-metal oxides) were tested and compared using methyl orange (MO) degradation experiments. It was found that M-Fe3O4@SiO2/ZnO had the best photocatalytic performance of the pure magnetite photocatalysts, with a MO removal rate of 91.5%, followed by 37.4% for M-Fe3O4@SiO2/NiO, 19.0% for M-Fe3O4@SiO2/Fe2O3, and 17.6% for M-Fe3O4@SiO2/CuO. The removal rates were 17.4% and 13.2% for the complex magnetite photocatalysts prepared from S-EPW and R-EPW, respectively. More than 98% of the heavy metals can be recovered from EPW through the simultaneous synthesis of the magnetite photocatalysts.