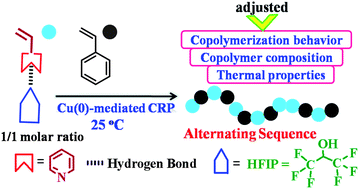
For the first time, reversible-deactivation radical copolymerization of 4-vinylpyridine (4VP) and styrene (St) was performed in a hydrogen bonding donor solvent, 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP). The copolymerization exhibited better control over the apparent number-average molecular weights than that in 2-propanol. With HFIP as a solvent, the reactivity ratios of 4VP and St were found to be 0.175 and 0.122, respectively, indicating a predominantly alternating sequence. The reactivity ratio of 4VP in HFIP was enhanced by 2.6 times compared with that in 2-propanol, producing a random copolymer. This well-regulated polymerization behavior as well as the monomer sequence were ascribed to electron induction and steric repulsion effects from the hydrogen bonding interaction between 4VP and HFIP. Moreover, the alternating copolymer of 4VP and St obtained in HFIP showed a slightly higher glass transition temperature with respect to that of the random copolymer obtained in 2-propanol.