Hybrid ligand–alkylating agents targeting telomeric G-quadruplex structures†
Filippo Doria,Matteo Nadai,Marco Folini,Marco Di Antonio,Luca Germani,Claudia Percivalle,Claudia Sissi,Nadia Zaffaroni,Stefano Alcaro,Anna Artese,Sara N. Richter,Mauro Freccero
Abstract
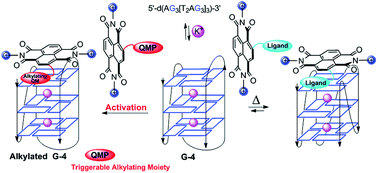
The synthesis, physico-chemical properties and biological effects of a new class of naphthalene diimides (NDIs) capable of reversibly binding telomeric DNA and alkylate it through an electrophilic quinone methide moiety (QM), are reported. FRET and circular dichroism assays showed a marked stabilization and selectivity towards telomeric G4 DNA folded in a hybrid topology. NDI–QMs’ alkylating properties revealed a good reactivity on single nucleosides and selectivity towards telomeric G4. A selected NDI was able to significantly impair the growth of melanoma cells by causing telomere dysfunction and down-regulation of telomerase expression. These findings points to our hybrid ligand–alkylating NDIs as possible tools for the development of novel targeted anticancer therapies.