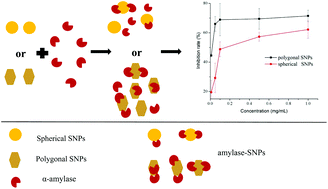
Nanoparticles are novel and fascinating materials for tuning the activities of enzymes. In this study, we investigated the influence of spherical and polygonal starch nanoparticles (SNPs) on α-amylase activity and revealed the reaction mechanisms by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence spectroscopy, and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. We discovered that both spherical and polygonal SNPs could inhibit the α-amylase activity, with half-inhibitory concentration values of 0.304 and 0.019 mg mL−1, respectively. Furthermore, spherical and polygonal SNPs followed competitive and mixed competitive inhibition mechanisms, respectively. The fluorescence data indicated that static quenching was dominant in the interaction between SNPs and α-amylase. The CD results demonstrated that the inhibition of α-amylase by SNPs was accompanied by the decreased intensity of the CD spectra of α-amylase. Our findings provide a novel strategy to inhibit α-amylase to reduce the digestion of starch, thus managing blood glucose levels.