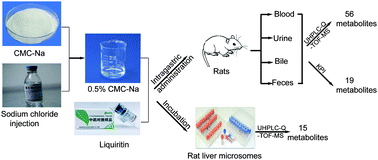
Liquiritin (LQ), the main bioactive constituent of licorice, is a common flavoring and sweetening agent in food products and has a wide range of pharmacological properties, including antidepressant-like, neuroprotective, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. This study investigated the metabolic pathways of LQ in vitro (rat liver microsomes) and in vivo (rat model) using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with hybrid triple quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). Moreover, supplementary tools such as key product ions (KPIs) were employed to search for and identify compounds. As a result, 56 in vivo metabolites and 15 in vitro metabolites were structurally characterized. Oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, methylation, acetylation, and sulfate and glucuronide conjugation were determined to be the major metabolic pathways of LQ, and there were differences in LQ metabolism in vitro and in vivo. In addition, the in vitro and in vivo metabolic pathways were compared in this study.