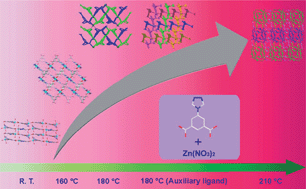
Five zinc(II) coordination polymers with 5-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (H2L), {[Zn2(L)2(H2O)4]·3H2O}n (1), {[Zn2(L)2(H2O)2]·3H2O}n (2), [Zn(L)(H2O)]n (3), [Zn(L)(H2O)]n (4) and {[Zn10(L)8(μ3-O)2(H2O)6]·8H2O}n (5), have been synthesized and structurally characterized. The compounds exhibit unprecedentedly high structural diversity. 1, 2, 3 and 5 are obtained by temperature-dependent synthesis and 4 is selectively induced by addition of 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid. In 1, the two-dimensional (2D) layers are further linked together by hydrogen bonds to form a three-dimensional (3D) supramolecular framework. 2 displays a non-interpenetrating (4,5)-connected 3D framework, while 3 and 4 present a pair of pseudopolymorphs with different interpenetrating structures. 3 is a two-fold interpenetrating hcb architecture while 4 shows a self-interpenetrating 3D msw-4-C2/c net. The results suggest that reaction temperature and auxiliary ligand play an important role to determine the resulting structures in this system. Furthermore, the photoluminescent, nonlinear optical and ferroelectric properties of the compounds were investigated.