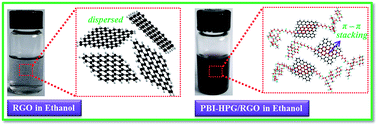
Perylene tetracarboxylic anhydride (PTCDA) was reacted with 6-aminocaproic acid to form the corresponding perylene bisimide (PBI). PBI was used as the foundation for oligomerisation of glycidol in a ring-opening reaction of glycidol leading to a hyper branched, water-soluble glycidol derivative of perylene (PBI-HPG). PBI-HPG was bound to the reduced graphene oxide via π–π stacking resulting in a compound termed PBI-HPG/RGO. The structure and morphology of PBI-HPG/RGO were investigated by infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), wide angle X-ray diffractometry (WAXD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). PBI-HPG/RGO was blended at different loadings in order to improve the thermal and mechanical properties of epoxy composites. The maximum Tg of the epoxy composites was about 20 °C and the decomposition temperature (Td) was 26 °C higher than that of neat epoxy. The incorporation of PBI-HPG/RGO yields a material with an impact strength of 39.6 kJ m−2 and a tensile strength at 0.7 wt%. It increased by 50.8% and 62.3%, respectively, compared to the neat epoxy.