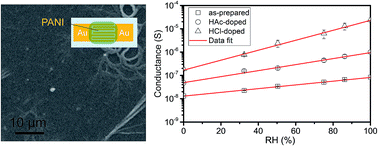
This article describes a simple method to prepare transferable polyaniline (PANI) thin films at the air–water interface. The method allows the convenient fabrication of dense and uniform PANI films at the nanoscale, and features high device performance of humidity sensors. The oxidation state of the interfacial PANI films (which closely relies on the conductivity of PANI films) could be optimized by controlling the concentration of aniline in the interfacial. The interfacial PANI thin film prepared from 0.04 M aniline solution (denoted the PANI-0.04 film) was employed for the evaluation of the sensitivity of the thin-film humidity sensor, resulting in 550% change in resistance with relative humidity (RH) ranging from 0% to 100%. The PANI-0.04 film sensor exhibited response (5–7 s) and recovery times (4–7 s) under dynamic tests, which correspond to excellent performance data among the PANI-based humidity sensor systems reported previously. Furthermore, the sensitivity of the PANI-0.04 film could be increased to 1900% and 14 000%, when the PANI-0.04 film was doped with acetic acid and hydrogen chloride, respectively.