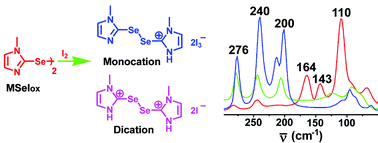
The inhibition of lactoperoxidase (LPO)-catalyzed iodination of L-tyrosine by the anti-thyroid drug methimazole (MMI) and its selenium analogue (MSeI) is described. MSeI inhibits LPO with an IC50 value of 12.4 µM, and this inhibition could be completely reversed by increasing the peroxide concentration. In addition to the inhibition, MSeI reacts with molecular iodine to produce novel ionic diselenides, and the nature of the species formed in this reaction appear to be solvent-dependent. The formation of ionic species in the reaction is confirmed by single-crystal X-ray studies, FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopic investigations. This study provides the first experimental evidence that MSeI not only effectively inhibits the LPO-catalyzed iodination of tyrosine, but also reacts with I2 to produce novel ionic diselenides. These results also suggest that MSeI reacts with iodine, even in its oxidized form, to form ionic diselenides containing iodide or polyiodide anions, which might be effective intermediates in the inhibition of thyroid hormones.