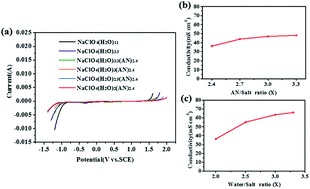
The practical application of aqueous sodium-ion batteries (ASIBs) is limited by the electrolysis of water, which results in a low working voltage and energy density of ASIBs. Here, a NaClO4-based acetonitrile/water hybrid electrolyte (NaClO4(H2O)2AN2.4) is applied to ASIBs for the first time, which effectively extends the electrochemical stability window (ESW) to 3.0 V and reduces the internal resistance of the battery. Based on this hybrid electrolyte, an ASIB full cell using carbon coated Na2.85K0.15V2(PO4)3 and NaTi2(PO4)3 as the cathode and anode materials, respectively, can afford a discharge capacity and energy density of 52 mA h g−1 and 51 W h kg−1, respectively, at a current density of 1 A g−1. The energy density of this battery exceeds almost all reported traditional ASIBs.