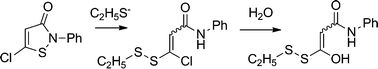
Isothiazolones and 5-chloroisothiazolones react chemoselectively with thiols by cleavage of the weak nitrogen–sulfur bond to form disulfides. They show selectivity for inhibition of the thiol-dependent cysteine protease cathepsin B and the histone acetyltransferase p300/CBP associated factor (PCAF) based on their substitution pattern. Furthermore, enzyme kinetics and mass spectroscopy indicate covalent binding of a 5-chloroisothiazolone to cathepsin B, which demonstrates their potential utility as probes for activity-based protein profiling.