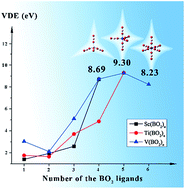
The equilibrium structures, stability and magnetic properties of Sc(BO2)n−/0 (n = 1–4) clusters were investigated on the basis of density functional theory calculations. The BO2 ligands prefer to stretch out in the most stable Sc(BO2)n− anions but tend to come together in the lowest-lying Sc(BO2)4 structure. According to the MP2 results, the Sc(BO2)4− species could be classified as hyperhalogen anions since they have larger vertical electron detachment energies (VDEs, 5.44–8.85 eV) than that of the superhalogen anion BO2−. With titanium and vanadium playing the role of central atom, the Ti(BO2)n−/0 (n = 1–5) and V(BO2)n−/0 (n = 1–6) clusters were studied in a similar manner. In these cases, the central transition metal atoms are inclined to keep their intrinsic spin. In addition, the hyperhalogen identity of the Ti(BO2)n− (n = 4, 5) and V(BO2)n− (n = 3–6) species were also confirmed by the calculated VDE values.