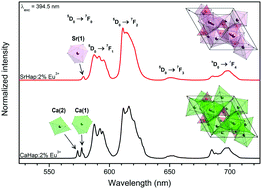
Calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHAp) and strontium hydroxyapatite (SrHAp) nanopowders doped with 2 mol% Eu3+ ions were obtained by using a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method and thermally treated in the temperature range from 450 to 950 °C for 3 h. XRD (X-ray powder diffraction) and TEM (transmission electron microscopy) techniques, as well as Raman and IR (infrared) spectroscopy, were used in order to determine the structural and morphological properties of the synthesized materials. The XRD patterns confirmed the crystal purity and nanometer size of the obtained materials. Nanoparticles were obtained as a function of the dopant concentration and annealing temperature in the size range from 50 nm for CaHAp samples to 80 nm for SrHAp samples. The luminescence properties of calcium and strontium hydroxyapatite doped with Eu3+ ions and their dependence on the annealing temperature were investigated in detail. Three distinct lines were observed for CaHAp samples and one line for SrHAp samples, which corresponded to 5D0 → 7F0 transitions. Moreover, a weak and broad emission corresponding to the 4f65d1 → 4f7 (8S7/2) transition of Eu2+ ions was observed in both cases. The Judd–Ofelt (J–O) theory was applied and a detailed analysis of the observed structural and spectroscopic measurements was performed and described.