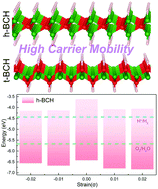
Although immense research on the extension of the two-dimensional (2D) material family has been carried out, 2D materials with a satisfactory band gap, high carrier mobility, and outstanding thermodynamic stability under ambient conditions are still limited. In this work, using first principles calculations, we proposed new 2D ternary materials consisting of C, B, and H atoms, namely hexagonal-BCH (h-BCH) and tetragonal-BCH (t-BCH). Both phonon calculations and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations show that these proposed sheets are thermodynamically stable phases. The electronic structure calculations indicate that h-BCH and t-BCH sheets are semiconductors with a band gap of 2.66 and 2.22 eV, respectively. Remarkably, the h-BCH (t-BCH) sheet exhibits electron mobility as high as 7.41 × 103 (1.09 × 103) cm2 V−1 s−1, which is higher than that of the MoS2 monolayer, though the hole mobility is about one (two) order of magnitude lower. Equally important is the fact that the position of both the conduction and valence band edges of the h-BCH sheet matches well with the chemical reaction potential of H2/H+ and O2/H2O, giving a 2D photocatalyst as a potential candidate for overall visible-light-driven water splitting. Therefore, the designed h-BCH and t-BCH monolayers have promising applications in future electronics and photocatalysts.