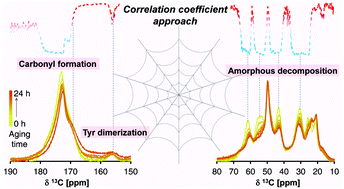
Recent successes in the production of recombinant spider silk have boosted numerous attempts for its industrialization as a robust and extremely tough material. In spite of the acceleration of the materials science, the inherent weakness of the spider silk against harsh environments has not been sufficiently addressed. Here, the thermal degradation of recombinant spider silk powder was systematically studied under an oxidative atmosphere, based on multilateral characterization including thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), chemiluminescence (CL), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), IR spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Spectroscopic changes throughout the degradation were analyzed using a spectral expression of correlation coefficients for resolving the structural and conformational modification of recombinant spider silk. The combination of the comprehensive characterization and statistical analysis clarified a crucial role of oxidative degradation. TGA exhibited a mass loss behavior of recombinant spider silk, typical for the auto-oxidation of polymers. Oxidation significantly promoted the decomposition of recombinant spider silk with chemiluminescence emission. We also identified the formation of carbonyl species as the main oxidation product, the preferential decomposition of amino acid residues in the amorphous phase, and aromatization and Tyr dimerization that could account for discoloration.