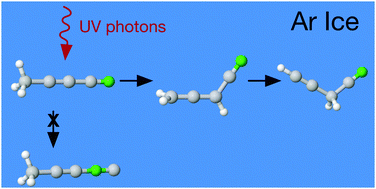
Cyanopropyne, CH3–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–CN, is a simple molecule whose photochemistry is still unexplored. Here we investigate the UV photolysis of this astrophysically significant nitrile trapped in solid argon. The FTIR study was assisted with 15N-isotopic substitution data and with DFT-level computations including the analyses of ground- and excited-state potential energy surfaces. Cyanopropyne was found to decay mainly via a two-step isomerization process. Infrared absorption spectra evolved to show signals from allenyl cyanide, CH2
C–CN, is a simple molecule whose photochemistry is still unexplored. Here we investigate the UV photolysis of this astrophysically significant nitrile trapped in solid argon. The FTIR study was assisted with 15N-isotopic substitution data and with DFT-level computations including the analyses of ground- and excited-state potential energy surfaces. Cyanopropyne was found to decay mainly via a two-step isomerization process. Infrared absorption spectra evolved to show signals from allenyl cyanide, CH2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–CN, which then further convert into propargyl cyanide, H–C
CH–CN, which then further convert into propargyl cyanide, H–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–CH2–CN. Some evidence for the presence of allenyl isocyanide, propargyl isocyanide, 3-cyanocyclopropene, and 1,2,3-butatrien-1-imine under particular experimental conditions was also observed. Although cyano/isocyano interconversion has been observed during photolysis of other closely related species in solid argon matrices, including H–C
C–CH2–CN. Some evidence for the presence of allenyl isocyanide, propargyl isocyanide, 3-cyanocyclopropene, and 1,2,3-butatrien-1-imine under particular experimental conditions was also observed. Although cyano/isocyano interconversion has been observed during photolysis of other closely related species in solid argon matrices, including H–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–CN, no evidence could be found for production of 1-isocyano-1-propyne, CH3–C
C–CN, no evidence could be found for production of 1-isocyano-1-propyne, CH3–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–NC for these experiments.
C–NC for these experiments.