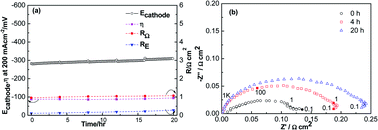
Strontium segregation in a La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ (LSCF) electrode reacts with Cr and S in a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC), which can cause cell performance deterioration. Integrated Cr and S poisoning for LSCF cathodes of SOFC was studied at 800 °C of 200 mA cm−2 (cathodic) for 20 h. After polarization in Cr and S at 800 °C for 20 h, polarization and ohmic resistances for LSCF were 2.4 Ω cm2 and 3.4 Ω cm2, which were larger than those for LSCF electrodes after Cr deposition only and S deposition only, respectively. The results illustrated that Cr and S deposition occurred on the surface of LSCF, which could form SrCrO4 and SrSO4. Compared to Cr deposition only and S deposition only, integrated Cr and S deposition was unsystematic, and the degradation phenomenon of Cr and S poisoning was more severe. The integrated Cr and S deposition of the LSCF electrodes was induced via interactions among CrO, SO2 and segregated SrO from LSCF.