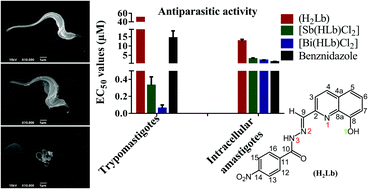
In the present work 8-hydroxyquinoline-derived hydrazones were obtained, namely 2-formyl-8-hydroxyquinoline-4-nitroimidazolhydrazone (H2Q4NO2Im) (H2La, 1) and 2-formyl-8-hydroxyquinoline-4-nitrobenzenehydrazone (H2Q4NO2Ph·H2O) (H2Lb, 2), as well as their antimony(III) [Sb(L)Cl2] (3, 4) and bismuth(III) [Bi(L)Cl2] (5, 6) complexes. The cytotoxic concentration range of the compounds was first determined in non-infected human and mouse cells. Furthermore, their antiparasitic activity against Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease, was evaluated. While H2Lb (2) was inactive, H2La (1) and complexes 3–6 inhibited T. cruzi trypomastigotes with EC50 values ranging from 0.06 to 30.05 μM. Complex 3 proved to be as potent as the reference drug benznidazole whereas complexes 4–6 were more potent than benznidazole as antiparasitic agents. The antimony(III) (4, EC50 = 0.33 μM) and bismuth(III) (6, EC50 = 0.06 μM) complexes presented the highest activities against the extracellular parasites. As expected, complexes 4 and 6 also exhibited the highest anti-T. cruzi activity against the amastigote form, with EC50 values of 3.05 and 2.31 μM, respectively. Investigation of the mode of action of complex 6 on trypomastigotes suggested the occurrence of cell death by necrosis.