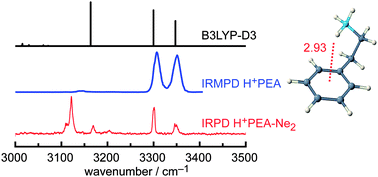
The structure and dynamics of the highly flexible side chain of (protonated) phenylethylamino neurotransmitters are essential for their function. The geometric, vibrational, and energetic properties of the protonated neutrotransmitter 2-phenylethylamine (H+PEA) are characterized in the N–H stretch range by infrared photodissociation (IRPD) spectroscopy of cold ions using rare gas tagging (Rg = Ne and Ar) and anharmonic calculations at the B3LYP-D3/(aug-)cc-pVTZ level including dispersion corrections. A single folded gauche conformer (G) protonated at the basic amino group and stabilized by an intramolecular NH+–π interaction is observed. The dispersion-corrected density functional theory calculations reveal the important effects of dispersion on the cation–π interaction and the large vibrational anharmonicity of the NH3+ group involved in the NH+–π hydrogen bond. They allow for assigning overtone and combination bands and explain anomalous intensities observed in previous IR multiple-photon dissociation spectra. Comparison with neutral PEA reveals the large effects of protonation on the geometric and electronic structure.