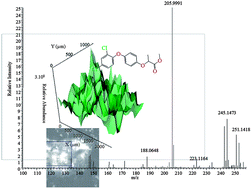
The paper reported a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric (MS) protocol for determination of herbicides, improving the analytical sample preparation step, making a significant contribution to the reproducibility and precision of the method. Matrix-analyte sampling is performed, employing low molecular weight (LMW) dication-containing organic crystals. Considering environmental control applications, six of the best selling herbicides, such as aclonifen (1), bifenox (2), diclofop-methyl (3), racemic mixture of diclofop (4), alachlor (5) and metolachlor (6) as well as their mixtures are quantified successively through the replacement of the polyfunctional benzoic acids with dication-containing organic matrices. The application of classical matrices for UV-MALDI-MS for the analysis of 1–6 caused their competitive chemical transformation, thus leading to spurious results and inaccurate analytical information, due to the wide variety of experimental conditions depending on the chemical, physico-chemical and physical nature of the herbicide analytes. The full method and technique validation, based on UV-MALDI-MS employing an Orbitrap analyser, are presented, achieving to our knowledge promising measurements for LMW analytes. These latter are judged by a fully validated analytical protocol based on positive electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry in a single and tandem (MS/MS) mode of operation. The chemical modifications, polymorph transformations of the UV-MALDI-MS crystal matrices and/or matrix-analyte samples, as well as ion-process formation upon solution → crystalline state and crystalline state → gas-phase transitions is controlled by joint application of unique and robust instrumental analytical methods for absolute structural determination, such as single crystal X-ray diffraction and mass spectrometry. As direct experimental qualitative, quantitative and structural evidence regarding the analytes was provided, the reported protocol is a fully validated one at each of the analytical steps. The additional quantum chemical data allowed correlation of the thermodynamic stability and MS abundances of observed ionic species in the gas-phase as well as the structure of crystals. Since environmental analysis involves a broad variety of analytes, conditions and degree of matrix complexity, only an individual certification method development may achieve meaningful analytical information. In this respect, the reported UV-MALDI-MS method for herbicides significantly impacts the field of environmental analytical chemistry, quality assurance and control; moreover the analytical protocol is constructed to deal with a real environmental problem. Therefore the reported method ensures real practical efficiency and reliability in the results for the human health safety, environmental monitoring and control programs.