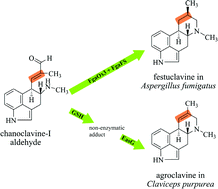
Ergot alkaloids are indole derivatives with diverse structures and biological activities. They are produced by a wide range of fungi with Claviceps purpurea as the most important producer for medical use. Chanoclavine-I aldehyde is proposed as a branch point via festuclavine or pyroclavine to clavine-type alkaloids in Trichocomaceae and via agroclavine to ergoamides and ergopeptines in Clavicipitaceae. Here we report the conversion of chanoclavine-I aldehyde to agroclavine by EasG from Claviceps purpurea, a homologue of the festuclavine synthase FgaFS in Aspergillus fumigatus, in the presence of reduced glutathione and NADPH. EasG comprises 290 amino acids with a molecular mass of about 31.9 kDa. The soluble monomeric His6-EasG was purified after overproduction in E. coli by affinity chromatography and used for enzyme assays. The structure of agroclavine was unequivocally elucidated by NMR and MS analyses.