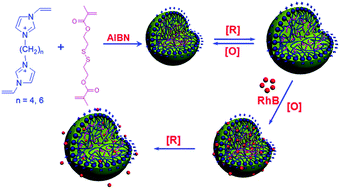
The unique disulfide chemistry has been widely explored for novel and versatile delivery systems addressing both intracellular and extracellular barriers. In this study, novel redox-responsive nanogels were fabricated by radical copolymerization of ionic liquid (IL)-based monomers, 1,n-butanediyl-3,3′-bis-1-vinylimidazolium dibromide ([CnVIm]Br, n = 4, 6), and disulphide dimethacrylate (DSDMA) in selective solvents. The as-synthesized nanogels were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analyses (TG), dynamic laser scattering (DLS) and zeta (ζ)-potential measurements. The results demonstrated that the sizes of poly(ionic liquid) (PIL)-based nanogels can be tuned by the feed ratio of the monomers and DSDMA. Moreover, the redox-response performances of these nanogels were evaluated through the size variation in the presence of dithiothreitol (DTT) and benzoyl peroxide (BPO). The capability of PIL-based nanogels for controlled release was also investigated by using rhodamine B (RhB) as prototype model drug. It was found that DTT-triggered release of RhB could be achieved. Therefore, a redox-triggered loading and release matrix can be conveniently fabricated via PIL-based nanogels. And it can also be potentially used as a controlled carrier in biological medicine.