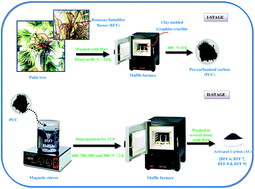
Activated carbon (AC) samples were prepared from the Borassus flabellifer flower (BFF) at different activation temperatures (600, 700, 800 and 900 °C) by a chemical activation method using H3PO4 as an activating agent. Scanning electron microscopy (HR-SEM) and X-ray analysis confirmed the surface morphology and the formation of graphite, and the amorphous nature of the activated carbon samples respectively. Fourier-infrared spectroscopy analysis provided the surface functional groups of the activated carbons. The BET specific surface area of the AC samples is found to be 633.43 m2 g−1 at an activation temperature of 900 °C. The dc conductivity was determined and the conductivity at ambient temperature was found to increase from 0.012 to 9.64 Ohm−1 cm−1. Electrochemical measurements were carried out using cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge–discharge (GCD) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) with a three-electrode system using 1 M KOH as an electrolyte, the active material (as-prepared AC) as a working electrode, Ag/AgCl as a reference electrode and platinum (Pt) as a counter electrode. The results indicate that BFF can potentially be applied as a precursor material for the production of low cost-high performance activated carbon electrode materials for electric double layer capacitors (EDLCs).