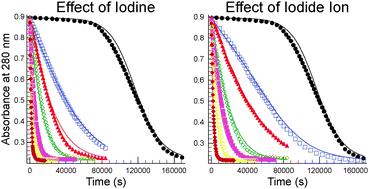
The tetrathionate–periodate reaction has been studied in presence of acetate–acetic acid buffer at T = 25 ± 0.1 °C and at I = 0.5 M ionic strength by a conventional diode array spectrophotometer. The stoichiometry of the reaction was found to be S4O2−6 + 7IO−4 + 3H2O → 4SO2−4 + 7IO−3 + 6H+. The profile of the measured absorbance–time curve is sigmoidal, having extremely long induction period that may be inferred as a classical type of autocatalysis, but surprisingly none of the products were proven to catalyze the reaction. Initial addition of micro amounts of iodine or iodide ion, however, strongly accelerates the reaction indicating that they are very efficient catalysts of the reaction. Moreover, it is also shown that the analyzing light beam has a great impact on the length of the induction period that questions the existence of the thermal reaction between tetrathionate and periodate. A 9-step kinetic model is presented and discussed that accurately takes the most important feature of the reaction into account.