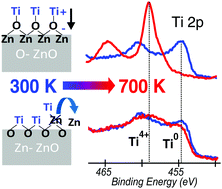
Orientation-dependent reactivity and band-bending are evidenced upon Ti deposition (1–10 Å) on polar ZnO(0001)–Zn and ZnO(000![[1 with combining macron]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) )–O surfaces. At the onset of the Ti deposition, a downward band-bending was observed on ZnO(000
)–O surfaces. At the onset of the Ti deposition, a downward band-bending was observed on ZnO(000![[1 with combining macron]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) )–O while no change occurred on ZnO(0001)–Zn. Combining this with the photoemission analysis of the Ti 2p core level and Zn L3(L2)M45M45 Auger transition, it is established that the Ti/ZnO reaction is of the form Ti + 2ZnO → TiO2 + 2Zn on ZnO(0001)–Zn and Ti + yZnO → TiZnxOy + (y − x)Zn on ZnO(000
)–O while no change occurred on ZnO(0001)–Zn. Combining this with the photoemission analysis of the Ti 2p core level and Zn L3(L2)M45M45 Auger transition, it is established that the Ti/ZnO reaction is of the form Ti + 2ZnO → TiO2 + 2Zn on ZnO(0001)–Zn and Ti + yZnO → TiZnxOy + (y − x)Zn on ZnO(000![[1 with combining macron]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) )–O. Consistently, upon annealing thicker Ti adlayers, the metallic zinc is removed to leave ZnO(0001)–Zn surfaces covered with a TiO2-like phase and ZnO(000
)–O. Consistently, upon annealing thicker Ti adlayers, the metallic zinc is removed to leave ZnO(0001)–Zn surfaces covered with a TiO2-like phase and ZnO(000![[1 with combining macron]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) )–O surfaces covered with a defined (Ti, Zn, O) compound. Finally, a difference in the activation temperature between the O-terminated (500 K) and Zn-terminated (700 K) surfaces is observed, which is tentatively explained by different electric fields in the space charge layer at ZnO surfaces.
)–O surfaces covered with a defined (Ti, Zn, O) compound. Finally, a difference in the activation temperature between the O-terminated (500 K) and Zn-terminated (700 K) surfaces is observed, which is tentatively explained by different electric fields in the space charge layer at ZnO surfaces.