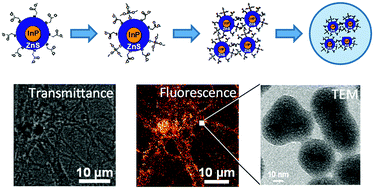
InP-based quantum dots (QDs) have been proposed as an alternative to CdSe-based QDs for both bioimaging and device displays. In this work, we incorporate hydrophilic InP/ZnS QDs into silica nanocapsules. The morphology, number of incorporated QDs, and photoluminescence (PL) properties of the capsules depend on the alkoxide hydrolysis conditions. By selecting a method of QD surface silanization, multiple QDs (typically 3) are incorporated into the nanocapsules (∼40 nm in size) without causing significant deterioration of the initial PL efficiency (up to 36%). Degradation analysis in different buffer solutions indicates that silica nanocapsules have higher stabilities than pristine QDs. The surface of the nanocapsules was modified with carboxyl groups without any change in morphology. Bright PL images with high resolution were obtained after introducing the nanocapsules into rat hippocampal neurons, when compared with commercial Q-trackers (polymer coated CdSe/ZnS QDs).